Categories > Garden Design and Planning
Edible Forest Gardens with Permaculture
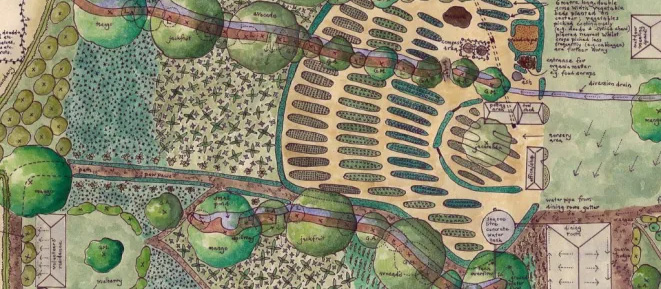
Edible forest gardens, rooted in the principles of permaculture, offer a sustainable and regenerative approach to gardening that mimics the structure and function of natural ecosystems. These gardens are designed to be not only beautiful but also productive, providing a diverse range of edible plants while enhancing ecological balance. In this article, we explore the concept of edible forest gardens and delve into the permaculture practices that make them flourish.
The Essence of Edible Forest Gardens
Edible forest gardens are a manifestation of the permaculture philosophy, which emphasizes working with nature rather than against it. In these gardens, plants are strategically arranged to imitate the layers of a natural forest, creating a harmonious and self-sustaining ecosystem. The key layers typically include:
- Canopy: Tall fruit or nut trees that provide shade and act as the uppermost layer.
- Understory Trees: Smaller trees and large shrubs that complement the canopy layer with additional yields.
- Shrubs: Berry bushes and medicinal plants that add diversity and attract beneficial insects.
- Herbaceous Plants: Perennials and annuals that cover the ground, preventing soil erosion and providing food.
- Root Crops: Tubers and root vegetables grown beneath the surface, adding another layer of productivity.
Permaculture Principles in Action
Permaculture, a portmanteau of "permanent" and "agriculture," is a design system that integrates sustainable agriculture, ecology, and social systems. When applied to edible forest gardens, permaculture principles create a resilient and regenerative environment. Some key permaculture practices include:
1. Polyculture:
Instead of relying on monoculture, where a single crop dominates, edible forest gardens embrace polyculture by planting a diverse array of species. This approach mimics natural ecosystems, reducing the risk of pests and diseases while promoting biodiversity.
2. Companion Planting:
Companion planting involves placing mutually beneficial plants near each other to enhance growth and repel pests. In edible forest gardens, companion planting is used strategically to create a balanced and harmonious ecosystem.
3. Mulching and Ground Cover:
Applying mulch and utilizing ground cover plants help retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil fertility. Permaculture encourages the use of organic materials like straw, leaves, and wood chips for effective mulching.
4. Water Conservation:
Permaculture promotes water-efficient techniques such as rainwater harvesting, swales, and contour planting. These methods ensure that water is used wisely and contributes to the overall sustainability of the garden.
Benefits of Edible Forest Gardens
Embracing the concept of edible forest gardens with permaculture principles yields numerous benefits for both the environment and the gardener. Some of these advantages include:
- Sustainability: Edible forest gardens are a sustainable form of agriculture, promoting ecosystem health and reducing reliance on external inputs.
- Food Security: Diverse plantings ensure a continuous supply of varied fruits, nuts, vegetables, and herbs, enhancing food security for the gardener.
- Biodiversity: The diverse range of plant species attracts beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
- Carbon Sequestration: Trees and perennial plants in edible forest gardens act as carbon sinks, helping mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Getting Started
Creating an edible forest garden requires thoughtful planning and a deep understanding of the local ecosystem. Start by assessing the soil, climate, and available space. Choose a variety of plants that are well-suited to your region and work together to create a resilient and thriving ecosystem.
Consider seeking guidance from experienced permaculturists, attending workshops, or joining local gardening communities to share knowledge and experiences. Remember that edible forest gardens evolve over time, so be patient and enjoy the journey towards a sustainable and bountiful garden.
By embracing the principles of permaculture in the creation of edible forest gardens, we not only cultivate food but also contribute to the health of the planet. These regenerative gardens serve as a testament to the possibilities of sustainable living and harmonious coexistence with nature.
Newsletter