Categories > Permaculture
Harmony in Cultivation: Exploring the Synergy of Permaculture and Agroforestry
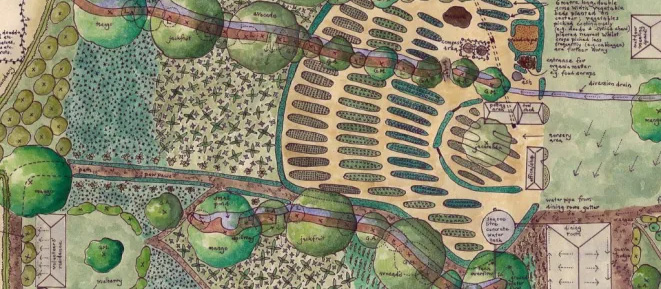
Gardening is not júst a hobby; it's a way of fostering harmony between humans and nature. In the pursuit of sustainable cultivation practices, permaculture and agroforestry stand out as beacons of ecological integrity and productivity. By integrating these two methodologies, gardeners can create vibrant, resilient ecosystems that yield abundant harvests while enhancing biodiversity and soil health.
Permaculture is a design system that mimics natural ecosystems to create self-sustaining environments. It emphasizes principles such as observation, diversity, and integration to maximize the productivity of the land while minimizing inputs and waste. In a permaculture garden, plants are carefully selected and arranged to fulfill multiple functions, such as providing food, shelter, and habitat for beneficial organisms. Agroforestry is the practice of integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes. By strategically planting woody perennials alongside crops, agroforestry systems harness the numerous benefits that trees offer, including shade, windbreaks, and nutrient cycling. Agroforestry fosters a dynamic relationship between different layers of vegetation, optimizing space and resource utilization. When permaculture and agroforestry principles are combined, they create a harmonious synergy that enhances the overall resilience and productivity of the garden. Permaculture provides the framework for designing diverse and resilient ecosystems, while agroforestry adds the dimension of incorporating trees and woody plants into the landscape. The integration of permaculture and agroforestry offers numerous benefits to gardeners: Integrating permaculture and agroforestry principles into your garden requires careful planning and implementation: As gardeners, we have the power to cultivate not just plants, but entire ecosystems that embody harmony and sustainability. By embracing the principles of permaculture and agroforestry, we can create gardens that are not only productive and beautiful but also resilient and regenerative, serving as models of sustainable living for generations to come.Understanding Permaculture
Exploring Agroforestry
The Synergy of Permaculture and Agroforestry
Benefits of Integration
Practical Implementation
Conclusion
Newsletter